[ad_1]
Followers of TV gear like to debate the deserves of flat-panel applied sciences. Previously, this meant evaluating Quantum Dot LED (or QLED TV because it’s mostly identified) and Natural LED, in any other case often known as OLED TV. However 2022 was the yr a brand new show know-how referred to as Quantum Dot OLED or QD-OLED, made its official debut, and it has already began to reshape the TV panorama due to new fashions from Sony and Samsung, and laptop screens from Dell’s Alienware model.
However what precisely is QD-OLED, how is it totally different from each QLED and OLED, and why do consultants assume it represents the most effective image high quality you may get? Let’s take a deep dive into the main points of QD-OLED and discover out.
What’s QD-OLED?
Merely put, QD-OLED is a hybrid show know-how that takes the already very spectacular qualities of OLED TV and improves its brightness and shade by means of using quantum dots.

The result’s a TV that reveals the gorgeous ranges of distinction and ideal blacks of OLED whereas delivering brightness ranges that exceed something we’ve seen from OLED to this point.
This “better of each worlds,” profit was largely theoretical till we bought an opportunity to see it for ourselves at CES 2022. These impressions survived even as soon as we introduced the primary two QD-OLED TVs in for testing. First with the Sony A95K, after which once more with the Samsung S95B. Each TVs earned a uncommon 10/10 ranking from our reviewer.
Image enhancements apart, it’s additionally potential that over time, QD-OLED TVs could show cheaper to purchase than equally sized OLED TVs. We’ll focus on this in additional element later. Since QD-OLED TVs are primarily an evolution of OLED, it’s anticipated that a few of the intelligent issues we’ve seen LG do with its OLED panels, like clear shows and rollable shows, will quickly be potential with QD-OLED, too.
How does QD-OLED work?
To know the internal workings of QD-OLED, we have to shortly clarify the variations between QLED and OLED.
QLED TV
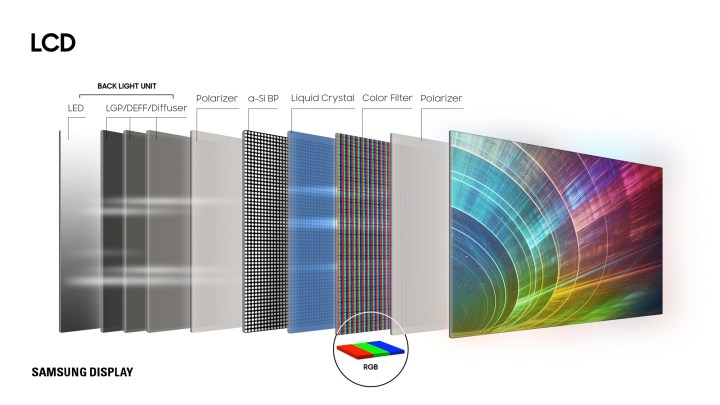
QLED TV makes use of 4 predominant components to provide its photos: An LED backlight, a layer of quantum dots, an LCD matrix, and a shade filter.
The LED backlight produces the entire brightness you see — and trendy LED backlights can produce quite a bit of brightness, way over OLED mild sources. However reaching that brightness whereas sustaining a full-spectrum white, is troublesome.
The answer: Begin with a very vivid blue LED mild supply, then use pink and inexperienced quantum dots to steadiness the blue right into a full spectrum of white. As a result of quantum dots could be tuned to emit particular colours and, amazingly, can do that at an almost 100% effectivity degree, QLED TVs get a much-needed enchancment to their shade accuracy with out sacrificing any brightness or needing to make use of extra vitality.
From there, the purified white mild passes by means of the LCD matrix (which is accountable for the pictures you see, and the way vivid or darkish areas of the display screen are) and, lastly, by means of the colour filter, which converts the white mild into the appropriate quantities of pink, inexperienced, and blue in order that we see true shade photos.

It’s system that produces vivid and really colourful photos. It’s additionally fairly inexpensive to provide as a result of, apart from the quantum dots, the entire elements have been round for many years, and at the moment are “low-cost” to make.
But it surely has drawbacks, too. Irrespective of how laborious the LCD matrix tries, it may’t block 100% of the sunshine from coming by means of in darkish scenes, so that you by no means get that good, inky black that you just see on an OLED TV. The LCD matrix additionally creates issues for off-angle viewing as a result of it tends to “tunnel” mild straight outward from the display screen.
QLED additionally has to make use of extra vitality to create the brightness you see as a result of the mixture of the LCD matrix and the colour filter diminishes the sunshine the LED backlight generates. This makes QLED TVs much less vitality environment friendly than OLED TVs.
Lastly, and this will likely solely matter to decor-oriented TV consumers, all of these components add as much as a thicker total TV panel.
OLED TV
OLED TV makes use of an OLED mild supply and a shade filter to provide its picture.
That sounds remarkably easy in comparison with QLED TV, and it’s. Because of the emissive nature of the fundamental factor of OLED TV — the OLED pixel — this one ingredient can maintain brightness and picture creation, primarily fulfilling the roles of each the LED backlight and the LCD matrix in QLED TV.
With out an LCD matrix, viewing angles with OLED TV are as near-perfect as we’ve ever seen. You may sit wherever you want and nonetheless see the identical ranges of brightness, distinction, and shade.
And as we’ve already hinted at, as a result of OLED pixels could be shut off utterly when a picture requires good blackness, that’s precisely what you get: No mild being emitted in any respect.
However OLED TV isn’t good both. You may solely derive a lot brightness from an OLED pixel. It’s wonderful in low-light circumstances, but it surely merely can’t compete with QLED’s devoted LED backlight in brighter environments. In case you’ve ever checked out a QLED and OLED TV aspect by aspect in a brightly lit Costco warehouse and located the QLED TV extra interesting, it’s most likely because of its superior brightness.

OLED TV brightness is decrease than QLED for 2 predominant causes. First, and most significantly, every OLED pixel creates its personal mild. However the extra energy you drive by means of an OLED pixel, the extra you shorten its lifespan. So OLED TVs might most likely get brighter than they do as we speak, however few consumers could be OK with a TV that solely lasted half as lengthy. The LEDs utilized in a QLED TV’s backlight are far much less vulnerable to this sort of getting old and might proceed to provide a number of mild for a very long time.
Second, regardless of how a lot mild an OLED pixel can create, a few of that mild will probably be absorbed by the colour filter.
OLED panels are additionally vulnerable to one thing often known as burn-in. In case you show the identical form of content material on an OLED TV for tons of consecutive hours — say a decrease information banner on a information channel, or a management panel in a online game — it may trigger these pixels to age at a quicker fee than the pixels which might be always displaying totally different photos.
The residual “shadow” of that static content material is known as burn-in, and as soon as it occurs, it’s normally everlasting.
Lastly, as a result of the large-format OLED panel market is successfully a monopoly, with only one firm — LG Show — manufacturing and promoting them to firms like LG, Sony, Philips, and Vizio, it can stay dearer than QLED for a while to come back.
QD-OLED: Busting the brightness barrier
So the query that faces the TV world is, how will you maintain on to all of OLED’s many advantages and enhance on its weaknesses?
The answer is QD-OLED, additionally referred to by some firms as “QD Show.”
Quantum Dot OLED considerably will increase the general brightness of OLED — and even improves its already excellent shade — by optimizing how a lot mild a single OLED pixel can emit and eliminating the colour filter.
Right here’s the way it works.
Why begin with white?
In the mean time, OLED TVs create their mild and shade place to begin with white mild. They do that by combining blue and yellow OLED materials to create a mix that comes very near pure white. Why do that as an alternative of utilizing pink, inexperienced, and blue OLED materials? The reply has to do with the complexities of producing OLED panels on the 50-inch to 88-inch sizes of as we speak’s TVs whereas maintaining prices as little as potential.
To offer you a way of simply how costly a real RGB OLED panel is, Sony makes a 4K, 55-inch monitor for the published and movie industries that makes use of this know-how. It prices almost $28,000.
However while you begin with white mild, you want a technique to separate the person pink, inexperienced, and blue parts of the spectrum. A shade filter does this admirably, however shade filters, as we talked about above, scale back brightness.
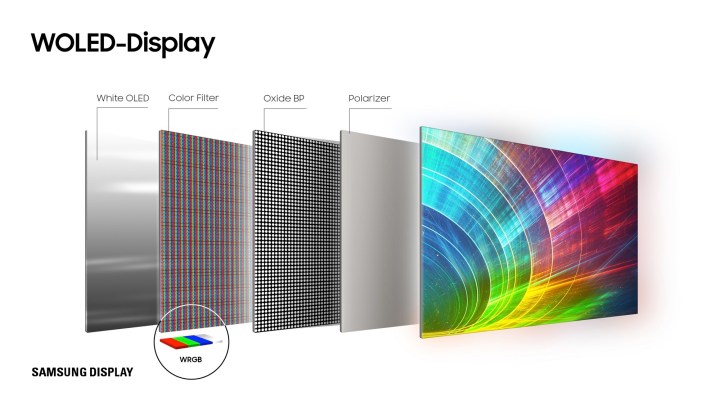

LG’s approach for regaining a few of the brightness misplaced to the colour filter includes using a white subpixel that bypasses the colour filter.
If you’re watching commonplace dynamic vary (SDR) content material, using that white subpixel is average. OLED TVs can simply get vivid sufficient to satisfy the complete specification for SDR with out relying closely on the brightness of the white subpixel.
“Shows of all kinds that use this structure are in a position to obtain shade accuracy at comparatively decrease luminance,” mentioned Jeff Yurek, director of selling and investor relations at Nanosys, an organization that develops quantum dot know-how. However HDR materials is a bit trickier.
When viewing HDR content material, the panels turbocharge these white subpixels to ship HDR’s increased brightness. However there’s a restrict to how laborious you may drive these white subpixels. Push them too far and never solely do you scale back the panel’s life, however that additional brightness may also wash out the colour of the opposite subpixels, one thing that’s particularly noticeable when displaying small options like textual content, which may typically look much less crisp.
Again to blue
To cope with the technical hurdles of OLED brightness, QD-OLED TVs take a web page out of QLED TV’s handbook. Utilizing the identical precept that lets a QLED TV flip a blue backlight right into a pure white mild utilizing pink and inexperienced quantum dots, a QD-OLED panel makes use of simply blue OLED materials as the premise of every pixel.
That blue OLED pixel is then divided into three subpixels: A blue subpixel, which is the unique blue OLED materials, left unchanged; a pink subpixel that layers red-tuned quantum dots over blue OLED; and a inexperienced subpixel that layers green-tuned quantum dots over blue OLED.

Since quantum dots are so energy-efficient, just about no brightness is misplaced in these two shade transformations. The result’s a real RGB OLED show with out the fee and complexity of a discrete RGB OLED place to begin, the brightness tax of a shade filter, or the necessity for a color-sapping white subpixel.
“What’s so thrilling about QD-OLED shows,” Yurek mentioned, “is that they don’t require a white subpixel to succeed in peak luminance. QD-OLED will have the ability to categorical the complete shade quantity from close to black all the best way as much as full-peak luminance with out compromise.”
Beginning small
If there’s one downside to QD-OLED in its present state of improvement, it’s that it doesn’t are available in all kinds of display screen sizes. As of December 2022, the largest QD-OLED TV you should purchase is a 65-inch 4K TV. There are not any 8K QD-OLED TVs (but).
That may change as extra folks purchase the first-generation merchandise and work on the manufacturing aspect continues to enhance, however for now, QLED and OLED have a significant benefit when it comes to measurement and backbone: each now exist in display screen sizes of as much as 98 inches, in as much as 8K decision.
QD-OLED: extra inexpensive?
It could take a number of years, but it surely’s potential that QD-OLED TVs will find yourself costing lower than OLED TVs to make. Eliminating the colour filter is an effective way to scale back supplies and manufacturing complexity, which ought to imply a smaller outlay of money.
And since QD-OLED will theoretically be brighter than OLED with out using extra electrical energy, it is perhaps potential to create QD-OLEDs which have the identical brightness as OLEDs whereas utilizing much less vitality. Decrease vitality use brings down the price of most of the elements that need to be engineered to deal with increased vitality masses.
This all assumes that the investments wanted to make QD-OLED manufacturing a actuality will probably be paid off shortly, however that’s removed from sure at this level.
Having your (OLED) cake and consuming it, too
Blue OLED materials — the sunshine supply of QD-OLED shows — is a notoriously tough substance to work with.
Very similar to different OLED supplies, there’s a three-way trade-off between lifespan, brightness, and effectivity. Usually talking, any time you prioritize one in all these attributes, the opposite two undergo. Drive an OLED pixel laborious sufficient to provide the brightness you need and also you not solely diminish its life expectancy but additionally its effectivity.
However QD-OLED shows could show to be the exception to this rule. By utilizing three layers of blue OLED materials per pixel, every layer can share the brightness burden.
“The quantity of energy wanted from the blue OLED pixel within the QD-OLED to provide a given quantity of front-of-screen brightness will probably be much less,” mentioned Jason Hartlove, CEO and president of Nanosys.
Who makes QD-OLED TVs?
- 1.
Samsung’s QD-OLED TV. - 2.
Sony’s QD-OLED A95K.
In the mean time, Samsung Show — a division inside Samsung that develops show applied sciences however doesn’t promote last merchandise like TVs or screens — is the one firm manufacturing QD-OLED panels. It sells these panels to firms like Sony, Dell’s Alienware division, and Samsung Electronics (the Samsung division that makes and sells TVs). We anticipate different firms will be part of the ranks of Samsung Show’s QD-OLED prospects now that the primary extremely constructive opinions are in.
We’re assured that there’ll finally be many firms promoting QD-OLED TVs, however for now, it seems like Sony and Samsung are alone on this new discipline.
When will QD-OLED TVs be in the stores?
You should purchase QD-OLED TVs proper now, from Samsung and Sony, however you could not understand it due to the best way every firm names its merchandise.
Sony’s QD-OLED is known as the Sony Bravia XR A95K 4K HDR OLED TV — no point out of “QD” or quantum dots. Samsung, bizarrely, does the identical factor with its QD-OLED TV, often known as the Samsung OLED 4K Good TV S95B.
Every mannequin at present is available in each 55- and 65-inch display screen sizes.
How a lot do they price?
Samsung’s QD-OLED TVs price significantly lower than Sony’s, although as Senior Editor, Caleb Denison, factors out, most individuals wouldn’t have the ability to respect the refined enhancements that Sony provides. This makes Sony’s worth premium troublesome to rationalize.
The Samsung OLED 4K Good TV S95B begins at $2,100 for the 55-inch mannequin, whereas the 65-inch model prices $2,800. Nevertheless, we’ve seen reductions of as much as $800 on these costs in 2022, so there are positively offers available.
For its half, Sony sells the 55-inch Bravia XR A95K 4K HDR OLED TV for $2,800 and the 65-inch for $3,500. Not solely are these common costs a lot increased than Samsung’s, however the reductions we’ve seen are additionally much less thrilling — solely about $200.
Is QD-OLED the final phrase in TV know-how?
Nope!
Nothing halts the progress of know-how, and the businesses that manufacture quantum dots have their sights set firmly on the eventual domination of the TV panorama.
QDEL sounds just like the holy grail of TV tech, doesn’t it?
Keep in mind after we mentioned that quantum dots use mild vitality at nearly 100% effectivity to provide their very own mild? Effectively, it seems that quantum dots aren’t choosy about their eating regimen. They may also be energized utilizing electrical energy for what’s often known as quantum dot electroluminescence, or QDEL. In our opinion, it’s QDEL panels that ought to be known as “QD Shows,” not QD-OLED panels, however this isn’t the primary time the trade has chosen a complicated tech identify, and it definitely received’t be the final.
Finally, this implies we’ll have the ability to ditch OLED and LED mild sources and create ridiculously skinny, versatile, colourful, vivid, and energy-efficient shows that by no means diminish in brightness or shade accuracy over time.
QDEL sounds just like the holy grail of TV tech, doesn’t it? However we’re not fairly there but. In the mean time, blue quantum dots possess the required attributes to behave as electroluminescent subpixels; nonetheless, pink and inexperienced quantum dots nonetheless want work.
MicroLED TVs are additionally changing into potent, if expensive, alternate options for the house show market. Their modular design signifies that their key energy is having the ability to scale from as small as 76 inches to nicely over 16 toes, however they’re additionally extremely vivid whereas possessing black ranges and shade accuracy to match QD-OLED TVs. However for now, they continue to be bulkier, are dearer, and pack decrease resolutions per inch than some other show know-how.
Samsung at present makes a 110-inch, 4K microLED TV, but it surely doesn’t promote the product on to consumers or by means of retail shops like Finest Purchase. As a substitute, it’s important to contact a Samsung-licensed AV installer. And if it’s important to ask how a lot it prices, nicely … you know the way that one goes.
Nonetheless, identical to QD-OLED, OLED, and plasma, it’s anticipated that microLED will quickly grow to be extra inexpensive, extra adaptable, and out there in sizes that the common purchaser would possibly need. Hold your eyes peeled and centered on all of the information popping out of CES 2023 for a peek at what’s to come back.
Editors’ Suggestions
[ad_2]
Source link




